Chen Tongqiang, etc. Agricultural engineering technology of greenhouse gardening Published in Beijing at 17: 30 on January 6, 2023.
Good rhizosphere EC and pH control are necessary conditions to achieve high yield of tomato in soilless culture mode in smart glass greenhouse. In this article, tomato was taken as the planting object, and the suitable rhizosphere EC and pH range at different stages were summarized, as well as the corresponding control technical measures in case of abnormality, so as to provide reference for the actual planting production in traditional glass greenhouses.
According to incomplete statistics, the planting area of multi-span glass intelligent greenhouses in China has reached 630hm2, and it is still expanding. Glass greenhouse integrates various facilities and equipment, creating a suitable growth environment for plant growth. Good environmental control, accurate irrigation of water and fertilizer, correct farming operation and plant protection are the four main factors to achieve high yield and high quality of tomatoes. As far as precise irrigation is concerned, its purpose is to maintain proper rhizosphere EC, pH, substrate water content and rhizosphere ion concentration. Good rhizosphere EC and pH satisfy the development of roots and the absorption of water and fertilizer, which is a necessary prerequisite for maintaining plant growth, photosynthesis, transpiration and other metabolic behaviors. Therefore, maintaining a good rhizosphere environment is a necessary condition for achieving high crop yield.
The out-of-control of EC and pH in rhizosphere will have irreversible effects on water balance, root development, root-fertilizer absorption efficiency-plant nutrient deficiency, root ion concentration-fertilizer absorption-plant nutrient deficiency and so on. Tomato planting and production in glass greenhouse adopts soilless culture. After water and fertilizer are mixed, the integrated delivery of water and fertilizer is realized in the form of dropping arrows. The EC, pH, frequency, formula, amount of return liquid and irrigation start time of irrigation will directly affect rhizosphere EC and pH. In this article, the suitable rhizosphere EC and pH in each stage of tomato planting were summarized, and the causes of abnormal rhizosphere EC and pH were analyzed and the remedial measures were summarized, which provided reference and technical reference for the actual production of traditional glass greenhouses.
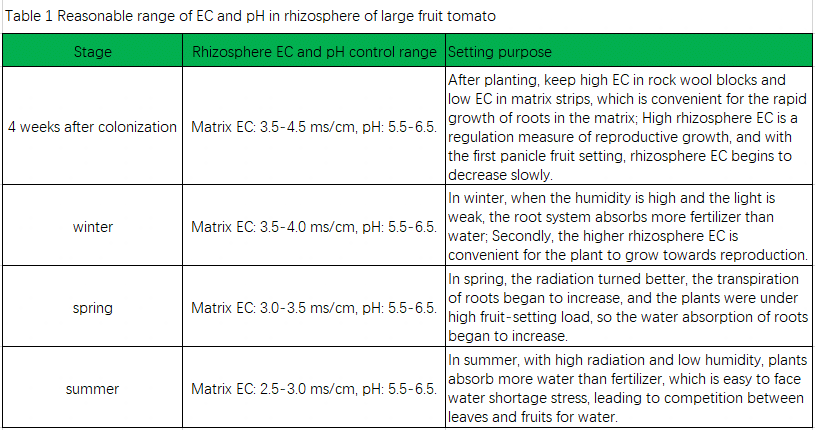
Suitable rhizosphere EC and pH at different growth stages of tomato
The rhizosphere EC is mainly reflected in the ion concentration of the main elements in the rhizosphere. The empirical calculation formula is that the sum of anion and cation charges is divided by 20, and the higher the value, the higher the rhizosphere EC. Suitable rhizosphere EC will provide suitable and uniform element ion concentration for root system.
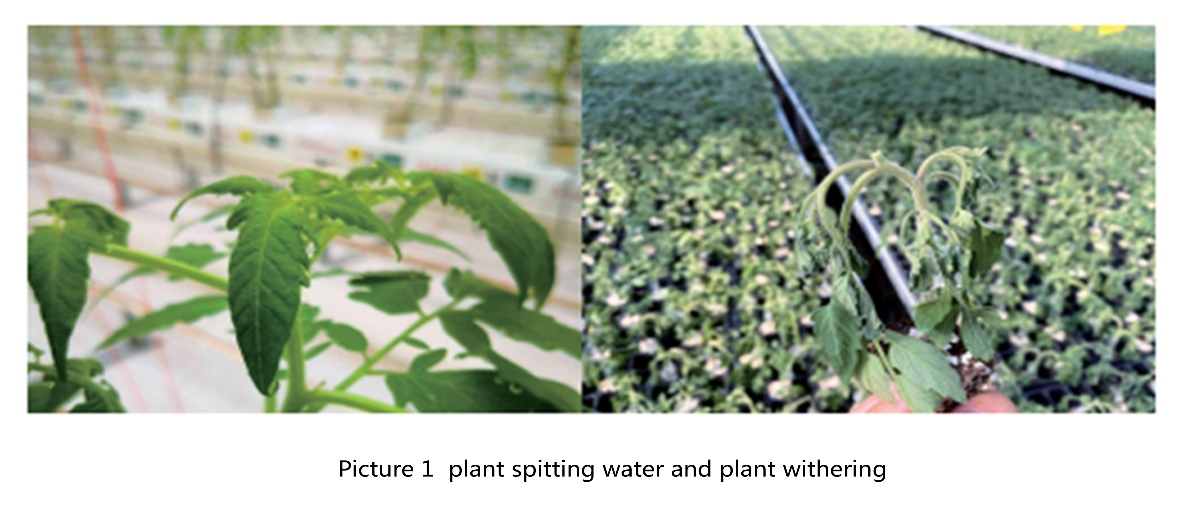
Generally speaking, its value is low (rhizosphere EC<2.0mS/cm). Because of the swelling pressure of root cells, it will lead to excessive demand for water absorption by roots, resulting in more free water in plants, and the excess free water will be used for leaf spitting, cell elongation-plant vain growth; Its value is on the high side (winter rhizosphere EC>8~10mS/cm, summer rhizosphere EC>5~7mS/cm). With the increase of rhizosphere EC, the water absorption capacity of roots is insufficient, which leads to water shortage stress of plants, and in severe cases, plants will wither (Figure 1). At the same time, the competition between leaves and fruits for water will lead to the decline of fruit water content, which will affect the yield and fruit quality. When the rhizosphere EC is moderately increased by 0~2mS/cm, it has a good regulatory effect on the increase of soluble sugar concentration/soluble solid content of fruit, the adjustment of plant vegetative growth and reproductive growth balance, so cherry tomato growers who pursue quality often adopt higher rhizosphere EC. It was found that the soluble sugar of grafted cucumber was significantly higher than that of the control under the condition of brackish water irrigation (3g/L of self-made brackish water with the ratio of NaCl:MgSO4: CaSO4 of 2:2:1 was added to the nutrient solution). The characteristics of Dutch’ Honey’ cherry tomato are that it maintains a high rhizosphere EC(8~10mS/cm) throughout the whole production season, and the fruit has a high sugar content, but the finished fruit yield is relatively low (5kg/m2).
Rhizosphere pH (unitless) mainly refers to the pH of rhizosphere solution, which mainly affects the precipitation and dissolution of each element ion in water, and then affects the effectiveness of each ion being absorbed by the root system. For most element ions, its suitable pH range is 5.5~6.5, which can ensure that each ion can be absorbed by the root system normally. Therefore, during tomato planting, the rhizosphere pH should always be maintained at 5.5~6.5. Table 1 shows the range of rhizosphere EC and pH control in different growth stages of large-fruit tomatoes. For small-fruit tomatoes, such as cherry tomatoes, the rhizosphere EC in different stages is 0~1mS/cm higher than that of large-fruit tomatoes, but all of them are adjusted according to the same trend.
Abnormal reasons and adjustment measures of tomato rhizosphere EC
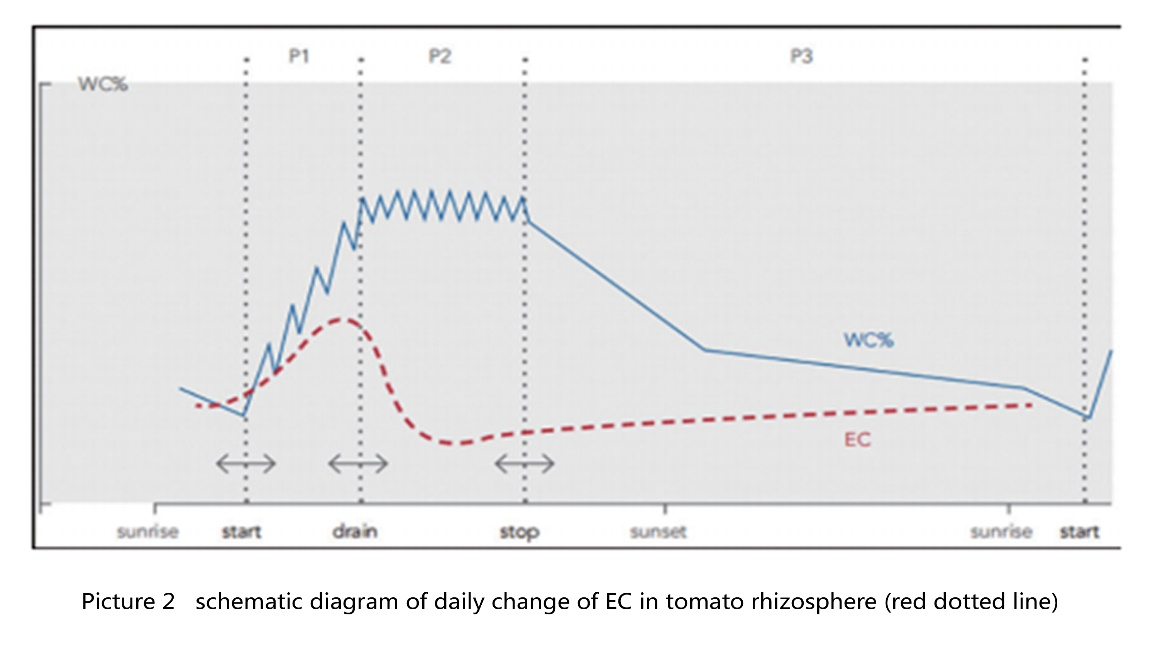
Rhizosphere EC refers to the EC of nutrient solution around the root system. When tomato rock wool is planted in Holland, growers will use syringes to suck nutrient solution from the rock wool, and the results are more representative. Under normal circumstances, the return EC is close to the rhizosphere EC, so the sample point return EC is often used as the rhizosphere EC in China. The diurnal variation of rhizosphere EC generally rises after sunrise, starts to decline and remains stable at the peak of irrigation, and slowly rises after irrigation, as shown in Figure 2.
The main reasons for the high return EC are low return rate, high inlet EC and late irrigation. The irrigation amount on the same day is less, which shows that the liquid return rate is low. The purpose of liquid return is to fully wash the substrate, ensure that the rhizosphere EC, substrate water content and rhizosphere ion concentration are in the normal range, and the liquid return rate is low, and the root system absorbs more water than elemental ions, which further shows the increase of EC. The high inlet EC directly leads to the high return EC. According to the rule of thumb, the return EC is 0.5~1.5ms/cm higher than the inlet EC. The last irrigation ended earlier that day, and the light intensity was still higher (300~450W/m2) after irrigation. Because of the transpiration of plants driven by radiation, the root system continued to absorb water, the water content of the substrate decreased, the ion concentration increased, and then the rhizosphere EC increased. When the rhizosphere EC is high, the radiation intensity is high, and the humidity is low, the plants are faced with water shortage stress, which is seriously manifested as withering (Figure 1, right).
The low EC in rhizosphere is mainly due to the high liquid return rate, the late completion of irrigation, and the low EC in liquid inlet, which will aggravate the problem. The high liquid return rate will lead to the infinite proximity between the inlet EC and the return EC. When irrigation ends late, especially in cloudy days, coupled with low light and high humidity, the transpiration of plants is weak, the absorption ratio of elemental ions is higher than that of water, and the decrease ratio of matrix water content is lower than that of ion concentration in solution, which will lead to low EC of return liquid. Because the swelling pressure of plant root hair cells is lower than the water potential of rhizosphere nutrient solution, the root system absorbs more water and the water balance is unbalanced. When transpiration is weak, the plant will be discharged in the form of spitting water (figure 1, left), and if the temperature is high at night, the plant will grow in vain.
Adjustment measures when the rhizosphere EC is abnormal: ① When the return EC is high, the incoming EC should be within a reasonable range. Generally, the incoming EC of large fruit tomatoes is 2.5~3.5mS/cm in summer and 3.5~4.0mS/cm in winter. Secondly, improve the liquid return rate, which is prior to the high-frequency irrigation at noon, and ensure that liquid return occurs every irrigation. The liquid return rate is positively correlated with the radiation accumulation. In summer, when the radiation intensity is still more than 450 W/m2 and the duration is more than 30 min, a small amount of irrigation (50~100mL/dripper) should be manually added once, and it is better that no liquid return occurs basically. ② When the liquid return rate is low, the main reasons are high liquid return rate, low EC and late last irrigation. In view of the last irrigation time, the last irrigation usually ends 2~5h before sunset, ending in cloudy days and winter ahead of schedule, and delaying in sunny days and summer. Control the liquid return rate, according to the outdoor radiation accumulation. Generally, the liquid return rate is less than 10% when the radiation accumulation is less than 500J/(cm2.d), and 10%~20% when the radiation accumulation is 500~1000J/(cm2.d), and so on.
Abnormal causes and adjustment measures of tomato rhizosphere pH
Generally, the pH of the influent is 5.5 and the pH of the leachate is 5.5~6.5 under ideal conditions. The factors that affect the rhizosphere pH are formula, culture medium, leachate rate, water quality and so on. When the rhizosphere pH is low, it will burn the roots and dissolve the rock wool matrix seriously, as shown in Figure 3. When the rhizosphere pH is high, the absorption of Mn2+, Fe 3+, Mg2+ and PO4 3- will be reduced, which will lead to the occurrence of element deficiency, such as manganese deficiency caused by high rhizosphere pH, as shown in Figure 4.
In terms of water quality, rainwater and RO membrane filtration water are acidic, and the pH of mother liquor is generally 3~4, which leads to the low pH of inlet liquor. Potassium hydroxide and potassium bicarbonate are often used to adjust the pH of inlet liquor. Well water and groundwater are often regulated by nitric acid and phosphoric acid because they contain HCO3-which is alkaline. Abnormal inlet pH will directly affect the return pH, so proper inlet pH is the basis of regulation. As for the cultivation substrate, after planting, the pH of the returning liquid of coconut bran substrate is close to that of the incoming liquid, and the abnormal pH of the incoming liquid will not cause drastic fluctuation of rhizosphere pH in a short time because of the good buffering property of the substrate. Under the rock wool cultivation, the pH value of the return liquid after colonization is high and lasts for a long time.
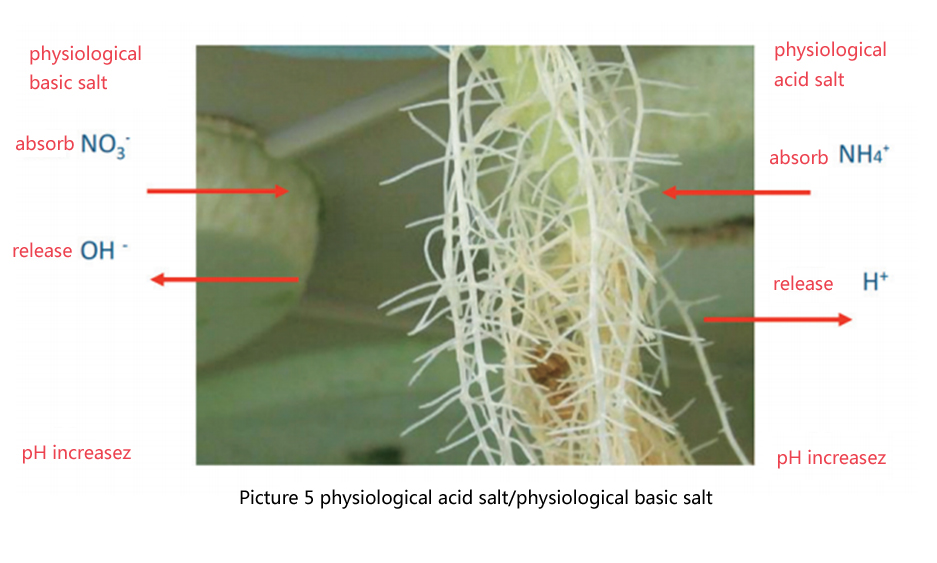
In terms of formula, according to the different absorption capacity of ions by plants, it can be divided into physiological acid salts and physiological alkaline salts. Taking NO3- as an example, when plants absorb 1mol of NO3-, the root system will release 1mol of OH-, which will lead to the increase of rhizosphere pH, while when the root system absorbs NH4+, it will release the same concentration of H+, which will lead to the decrease of rhizosphere pH. Therefore, nitrate is a physiologically basic salt, while ammonium salt is a physiologically acidic salt. Generally, potassium sulfate, calcium ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate are physiological acid fertilizers, potassium nitrate and calcium nitrate are physiological alkaline salts, and ammonium nitrate is neutral salt. The influence of liquid return rate on rhizosphere pH is mainly reflected in the flushing of rhizosphere nutrient solution, and the abnormal rhizosphere pH is caused by the uneven ion concentration in rhizosphere.
Adjustment measures when rhizosphere pH is abnormal: ① First, check whether the pH of influent is in a reasonable range; (2) When using water containing more carbonate, such as well water, the author once found that the pH of the influent was normal, but after the irrigation ended that day, the pH of the influent was checked and found to be increased. After analysis, the possible reason was that the pH was increased due to the buffer of HCO3-, so it is recommended to use nitric acid as a regulator when using well water as irrigation water source; (3) When rock wool is used as planting substrate, the pH of the return solution is high for a long time in the early stage of planting. In this case, the pH of the incoming solution should be appropriately reduced to 5.2~5.5, and at the same time, the dosage of physiological acid salt should be increased, and calcium ammonium nitrate should be used instead of calcium nitrate and potassium sulfate should be used instead of potassium nitrate. It should be noted that the dosage of NH4+ should not exceed 1/10 of the total N in the formula. For example, when the total N concentration (NO3- +NH4+) in the influent is 20mmol/L, the NH4+ concentration is less than 2mmol/L, and potassium sulfate can be used instead of potassium nitrate, but it should be noted that the concentration of SO42- in the irrigation influent is not recommended to exceed 6~8 mmol/L; (4) In terms of liquid return rate, the irrigation amount should be increased each time and the substrate should be washed, especially when rock wool is used for planting, so the rhizosphere pH can not be adjusted quickly in a short time by using physiological acid salt, so the irrigation amount should be increased to adjust the rhizosphere pH to a reasonable range as soon as possible.
Summary
A reasonable range of rhizosphere EC and pH is the premise to ensure the normal absorption of water and fertilizer by tomato roots. Abnormal values will lead to plant nutrient deficiency, imbalance of water balance (water shortage stress/excessive free water), root burning (high EC and low pH) and other problems. Because of the delay of plant abnormality caused by abnormal rhizosphere EC and pH, once the problem occurs, it means that abnormal rhizosphere EC and pH have occurred for many days, and the process of plant returning to normal will take time, which directly affects the output and quality. Therefore, it is important to detect the EC and pH of the incoming and returned liquid every day.
END
[Cited information] Chen Tongqiang, Xu Fengjiao, Ma Tiemin, etc. Rhizosphere EC and pH control method of tomato soilless culture in glass greenhouse [J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2022,42(31):17-20.
Post time: Feb-04-2023